什么是子宫内膜异位症?
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside of it, causing pain and discomfort.
Endometriosis is a persistent medical condition where tissue that resembles the lining of the uterus is located outside of the uterus. This tissue is typically linked with monthly menstruation and is known for causing abnormally heavy and painful periods, pelvic pain, severe cramping, and discomfort during sex (dyspareunia). The growths are typically non-cancerous, inflammatory, and stem-cell driven, and their progression can depend on estrogen levels.
Around 176 million women globally are affected by endometriosis, making it a significant cause of chronic pelvic pain and infertility. Endometriosis has been associated with other health issues, such as certain autoimmune diseases, cancers, fibroids, adenomyosis, and interstitial cystitis. It is also a leading reason for laparoscopic surgery and hysterectomy in the United States. The disease has a substantial economic impact, with businesses losing billions of dollars each year due to compromised productivity and absenteeism caused by endometriosis.
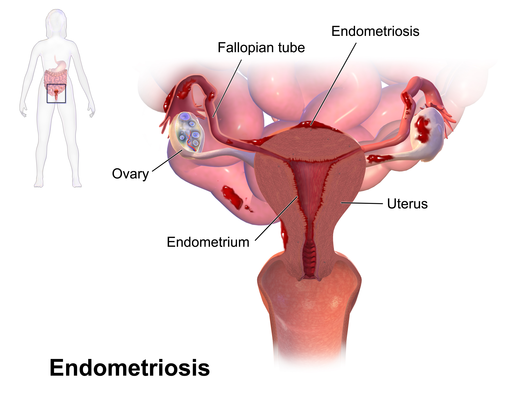
Endometriosis (Image source: Blausen Medical, 2014)
子宫内膜异位症发生在哪里?
Endometriosis occurs when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside of the uterus, often in other areas of the pelvis such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, bowel, bladder, or the lining of the pelvis itself.
It is frequently found on the top of the vagina (anterior cul-de-sac) and in the peritoneal cavity between the rectum and the posterior wall of the uterus (posterior cul-de-sac).
In some exceptional instances, it may spread to other areas of the body, including the diaphragm, lungs, kidney, appendix, and even the gastrocnemius muscles in the calf.
子宫内膜异位症的原因
The exact cause of endometriosis is not yet fully understood, but there are several theories.
One theory suggests that it may occur due to retrograde menstruation, where menstrual blood and endometrial tissue flow back through the fallopian tubes and into the pelvis during menstruation.
Another theory suggests that it may be caused by genetics or a problem with the immune system that allows the endometrial tissue to grow outside the uterus. Hormonal factors, such as excess estrogen production, may also contribute to the development of endometriosis.
However, the precise cause or causes of endometriosis remain a subject of ongoing research.
子宫内膜异位症的症状
Endometriosis can manifest in various symptoms, with pain being the primary indicator. This pain may vary from mild to severe and typically affects the abdomen, pelvic region, and lower back.
While some individuals with endometriosis may not experience symptoms, others may encounter:
- painful menstrual cramps
- abdominal or back pain during and in between periods
- pain during intercourse
- heavy bleeding
- spotting between periods
- infertility
- painful bowel movements.
The severity of the symptoms does not necessarily correspond with the extent of the endometriosis; a person with limited patches may experience severe pain while someone with severe endometriosis may not have much discomfort.
子宫内膜异位症的阶段
Endometriosis can be classified into four stages or types, based on the location, size, and depth of the endometrial tissue growth:
- Minimal or Stage 1: In this stage, there are small lesions or shallow implants on the surface of the ovary and pelvic lining.
- Mild or Stage 2: In this stage, there are more lesions and deeper implants in the pelvic lining and on the ovary.
- Moderate or Stage 3: This stage involves deep implants on the pelvic lining and ovaries, as well as the formation of adhesions (scar tissue) between organs.
- Severe or Stage 4: This is the most advanced stage of endometriosis, in which deep implants and adhesions are widespread throughout the pelvic cavity, affecting multiple organs such as the bladder, rectum, and intestines.
It is important to note that the stage of endometriosis does not necessarily correlate with the severity of symptoms, as individuals with minimal endometriosis may experience significant pain while those with severe endometriosis may be asymptomatic.
子宫内膜异位症的诊断
What is the Initial Step in Diagnosing Endometriosis?
To determine whether imaging tests are necessary, it is recommended to first consult with a GYN physician who is experienced in diagnosing endometriosis and can perform a thorough pelvic exam, including a discussion of your symptoms and medical history.
What Imaging Test are Available?
There are several imaging tests that can be used to help diagnose endometriosis. These include transvaginal ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and computed tomography (CT) scan.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound is a type of imaging test that may be used to diagnose or evaluate endometriosis. It involves inserting an ultrasound wand into the vagina to create images of the reproductive organs and surrounding structures. This can help to identify the presence of endometriotic cysts or lesions in the ovaries or other areas. However, it is important to note that not all cases of endometriosis can be detected through ultrasound, and other imaging tests or diagnostic procedures may be necessary.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can also be used to diagnose endometriosis. This imaging technique uses a powerful magnet and radio waves to create detailed images of the inside of the body. It can provide information on the location and extent of endometriosis lesions, as well as identify any potential complications such as cysts or adhesions. An MRI can also be useful in ruling out other conditions that may be causing similar symptoms. However, MRI is not typically used as a first-line diagnostic tool for endometriosis and may be more expensive and time-consuming than other imaging tests.
Gold Standard for Diagnosing Endometriosis
Laparoscopy is a surgical procedure that is commonly used to diagnose and treat endometriosis. During a laparoscopy, a surgeon makes a small incision near the navel and inserts a thin, lighted instrument called a laparoscope into the abdomen. The laparoscope allows the surgeon to view the pelvic organs and look for signs of endometrial tissue outside the uterus. If endometriosis is found, the surgeon may also remove the tissue during the same procedure.
Laparoscopy is considered the gold standard for diagnosing endometriosis.
子宫内膜异位症治疗的手术方法
治疗子宫内膜异位症的手术方法有多种,包括腹腔镜切除术、机器人辅助腹腔镜检查和剖腹手术。使用的具体方法取决于子宫内膜组织的严重程度和位置,以及患者的整体健康状况和偏好。一般来说,子宫内膜异位症手术的目标是切除受影响的组织,同时尽可能保留健康的组织和器官。
腹腔镜切除术
Laparoscopic excision is a surgical procedure that can be used to remove endometriosis tissue from the body. It involves making small incisions in the abdomen and inserting a laparoscope (a thin, lighted tube with a camera) to visualize the internal organs. Surgical instruments are then used to remove the endometrial tissue. This procedure is considered the gold standard for diagnosing and treating endometriosis.
The cost of laparoscopic excision of endometriosis can vary depending on the location, healthcare provider, and type of insurance. It’s recommended to request an appointment with New York Gynecology Endometriosis (NYGE) to obtain an accurate estimate of the cost.
机器人辅助腹腔镜检查
Robotic-assisted laparoscopy is a type of laparoscopic surgery that uses a computer-controlled robot to perform the surgery. It is a minimally invasive surgical option that can be used to diagnose and treat endometriosis. The cost of robotic-assisted laparoscopy for endometriosis will vary depending on factors such as the hospital or surgical center, surgeon fees, and insurance coverage.
However, in general, robotic-assisted laparoscopy is often more expensive than traditional laparoscopy due to the use of the robot and the associated technology.
剖腹手术
Laparotomy is a surgical procedure that involves making a large incision in the abdominal wall to gain access to the pelvic organs. It is used to diagnose and treat a variety of conditions, including endometriosis. During laparotomy for endometriosis, the surgeon will make an incision in the abdominal wall, and then carefully remove the endometrial tissue. Laparotomy is a more invasive surgery than laparoscopy and is typically reserved for cases where the endometrial tissue is widespread or in hard-to-reach areas.
However, it may also be recommended in cases where a woman has a large mass or adhesions that need to be removed. The recovery time for laparotomy is longer than that for laparoscopy.
The cost of laparotomy can vary depending on the location, healthcare provider, and individual circumstances.
Non-surgical methods for endometriosis treatment
Although non-surgical treatments like NSAIDs, progestin-only birth control pills, and GnRH analogs can alleviate some symptoms of endometriosis, they are usually temporary and do not provide a complete cure for the disease. The most effective approach to treating endometriosis involves undergoing laparoscopic deep excision surgery and a comprehensive multidisciplinary treatment plan.
Pankaj Singhal, MD, MS, MHCM
机器人手术外科医生大师
Pankaj Singhal 博士是全球公认的子宫内膜异位症外科医生,在腹腔镜切除手术方面拥有超过 25 年的专业知识,这使他能够充满信心地应对最具挑战性的子宫内膜异位症病例。 Pankaj 医生治疗患有多种子宫内膜异位症相关疾病的患者,从卵巢子宫内膜异位症到影响肠道和其他器官的严重深部浸润性子宫内膜异位症。
Pankaj 医生优先考虑微创手术并提供全面的个人护理。此外,他还是纽约妇科和子宫内膜异位症 (NYGE) 的所有者和创始人,并一生致力于倡导、尊重和治疗患有这种鲜为人知的疾病的女性。他是全美国少数完成超过 5,718 例机器人辅助妇科手术的外科医生之一。
我们接受大多数主要保险计划
便捷的计费选项,全面覆盖。
手术通常由健康保险承保。然而,承保范围可能会有所不同,具体取决于具体的保险计划和保单。一些保险计划可能涵盖广泛的外科手术,包括选择性和必要的手术,而其他保险计划可能对某些手术有限制或排除。
在某些情况下,某些保险计划或计划可能会全额承担手术费用,使患者无需承担经济责任。
请求预约
New York Gynecology Endometriosis
"*" indicates required fields
